 A legal fight for the integrity and public oversight of elections in the Peach State has been running in federal court for nearly eight years now. As we've reported over those years here on The BradCast, it began long before Trump and his Republican MAGA stooges dreamt up their imaginary 'Stop the Steal' scheme to pretend the 2020 election was stolen from them. The long-running suit has highlighted vulnerabilities and revealed criminal actions along the way. But, as of last night, the case may have come to an end. Our guest today, however, a lead Plaintiff in the case, vows: "This fight is far from over." [Audio link to full show follows this summary.]
A legal fight for the integrity and public oversight of elections in the Peach State has been running in federal court for nearly eight years now. As we've reported over those years here on The BradCast, it began long before Trump and his Republican MAGA stooges dreamt up their imaginary 'Stop the Steal' scheme to pretend the 2020 election was stolen from them. The long-running suit has highlighted vulnerabilities and revealed criminal actions along the way. But, as of last night, the case may have come to an end. Our guest today, however, a lead Plaintiff in the case, vows: "This fight is far from over." [Audio link to full show follows this summary.]
FIRST UP... The madness wrought by our last election continues today, however, as layoffs begin for thousands of workers in agencies overseen by the Dept. of Health and Human Services (HHS), now directed by vaccine conspiracist Bobby Kennedy, Jr. "The cuts include researchers, scientists, doctors, support staff and senior leaders, leaving the federal government without many of the key experts who have long guided U.S. decisions on medical research, drug approvals and other issues" at the CDC, NIH, FDA and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, among others, AP reports today. A coalition of Democratic state Attorneys General are now suing to block the scheme, which they describe as unlawful, charging it will result in "serious harm to public health" and put states "at greater risk for future pandemics and the spread of otherwise preventable disease, while cutting off vital public health services."
Raising attention to madness like that was just one of the reasons that New Jersey's Democratic U.S. Senator Corey Booker determined he needed to take and hold the floor of the U.S. Senate "as long as I am physically able." As of airtime, he was on the brink of breaking the all-time, 24-hour and 18-minute record for holding the Senate floor. Shortly after airtime today, he did so, before standing down after just over 25 hours. We share some of his remarks.
THEN... We've been waiting for this federal court ruling for more than a year since its 17-day trial in January of 2024. In fact, we've been waiting for it for almost eight years, since it was first filed in 2017, challenging Georgia's use of 100% unverifiable touchscreen voting systems. The state was the first, along with Maryland, to do so statewide back in 2002.
In 2019, the judge overseeing the case, U.S. District Judge Amy Totenberg, determined the state's Diebold touchscreen voting systems were so error-prone, unverifiable and vulnerable to manipulation, that she ordered they may no longer be used. In 2020, Georgia's current Sec. of State, Brad Raffensperger, defied voting system and cybersecurity experts who advised him to move the state to a hand-marked paper ballot system. Instead, with the blessing of former SoS, now Governor Brian Kemp, he moved to a new, unverifiable touchscreen voting system made by Dominion, at a price tag of more than $100 million to taxpayers. It has since proven to have many of the same vulnerabilities as the old Diebold systems. Last year's trial revealed many of those flaws.
But last night, well over a year since the trial in an Atlanta federal courtroom concluded, Judge Totenberg finally issued her 33-page ruling [PDF], lauding the plaintiffs for their "dedication to ensuring that Georgia's elections are conducted in a transparent, safe, and reliable manner," before dismissing the case entirely due to what she described as a lack of standing by the Plaintiffs to bring the suit in the first place. "Ultimately, Plaintiffs failed to establish at trial that Georgia's continued use of the [touchscreen Ballot Marking Device] will likely cause them to suffer a legally cognizable injury," she wrote in her order's Conclusion. "The Court therefore lacks jurisdiction to consider the merits of Plaintiffs' claims."
"Although Plaintiffs have not ultimately prevailed on their legal claims, their work has identified substantial concerns about the administration, maintenance, and security of Georgia's electronic in-person voting system," Totenberg ruled. "These investigative and educational efforts have prompted meaningful legislative action to bolster the transparency and accountability of Georgia's voting systems."
We're joined today --- as we have been many times over the years to discuss this case, and its many startling revelations and news-breaking findings --- by longtime election security and transparency champion, MARILYN MARKS, Founder and Executive Director of the non-profit good government group, Coalition for Good Governance, one of the case's lead Plaintiffs. Marks seemed as gobsmacked, confused and disappointed by all of this today as we were in the hours since last night's release of the judge's order.
"We haven't really absorbed this blow yet," she tells me. "After eight years to find out, 'Oh, you had no business to be here to begin with, here in court.'" Marks did her best, nonetheless, to explain the court's ruling. "She's basically said, 'You've got the right to vote. You've got the right to cast a ballot. But you don't have the right to know who you're voting for.'" That, a reference to the unreadable QR codes printed out on each ballot by Dominion's touchscreens, supposedly containing the voter's ballot selections. That QR code cannot be read or approved for accuracy by voters, however. Instead, they are asked to verify their selections on the human-readable portion of the computer-marked paper. But those selections are not used to tabulate election results.
Marks cites a 2022 race in which voters for Michelle Long-Spears, a candidate for Georgia's DeKalb County Commission, selected the candidate's name on the touchscreen, saw it on the computer-printed ballot as their selection, but could not tell that the QR Code actually registered a vote for her opponent.
Throughout the years-long course of this case, Marks, in her role as Plaintiff, helped reveal a number of troubling matters, from the fact (as demonstrated in court) that voters at the polling place are able to hack GA's Dominion touchscreens with no more than a ballpoint pen; to expert findings that resulted in a warning about these systems issued by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency; to the tape-recorded confession she obtained from an Atlanta businessman who detailed his role in a scheme to unlawfully access and copy the code for the proprietary statewide voting system in Coffee County, GA, and share it over the Internet with fellow MAGAs after the 2020 election. That man, Scott Hall, was one of several criminal co-conspirators charged along with Donald Trump in Fani Willis' RICO case against him and 18 others. Hall, Sidney Powell and other Trumpers pleaded guilty. Marks was the one who first revealed the now notorious Coffee County breach during the course of the case that was dismissed last night.
"Back in her decision in the Fall of 2020," as part of this case, Marks explains today, "right before the 2020 election, [Judge Totenberg] was saying that with these [new Dominion] systems, it is a matter of when, not if, this system is going to be hacked. She talked about how it cannot be audited. She went through many, many warnings for the state, that essentially this was not a good system. She seemed to agree with us on the merits for the last eight years, but now says, 'You shouldn't have been here anyway.'"
Marks asserts that Totenberg appeared to agree with Plaintiffs on the merits throughout the case and its eventual trial, as attorneys for the State, representing Raffensperger, failed to rebut Plaintiff's many world-class voting system experts and their testimony. "I don't think I read anything where she felt that [Raffensperger] presented compelling facts. Our experts presented unrebutted facts. [The state's attorneys] really had nothing other than, 'You guys are election deniers. You don't have standing. Y'all haven't really been hurt.' There was really no rebuttal on the experts' findings."
In fact, despite claims by the State, the Plaintiffs in this case never challenged the results of any election. Rather, they presented an airtight case that the systems used in Georgia can be manipulated, violate voter secrecy rights, and can't be known to reflect the intent of any voter after an election. Those unrebutted facts, which Totenberg appears to have agreed with, were not enough to overcome her final ruling --- after nearly eight years and countless findings in favor of the Plaintiffs --- that they can't show they suffer any harm with the use of these systems.
Marks says she is still discussing the matter with attorneys, but suggested she may appeal the case to the 11th Circuit Court of Appeals which has already, in a previous ruling in this case, agreed that Plaintiffs did, in fact, have standing.
For the record, Republican state lawmakers enacted a law last year that bars the use of QR Codes on ballots by 2026. Marks, however, explains why that provision is likely to put upcoming elections at legal risk and is unlikely be effectuated, as the state Legislature has, to date, failed to appropriate the nearly $70 million the law calls for to only somewhat correct Raffensperger's Touchscreen Follies.
FINALLY... Desi Doyen joins us for our latest Green News Report, as the Trump Administration declares they will be shutting down FEMA (in this middle of this year's hurricane season!); is closing coal mine safety offices around the county; and overturning landmark fees on oil and gas drillers' climate-warming methane pollution...
(Snail mail support to "Brad Friedman, 7095 Hollywood Blvd., #594 Los Angeles, CA 90028" always welcome too!)
|


 Trump EPA Guts Enviro Justice Office: 'BradCast' 4/24/25
Trump EPA Guts Enviro Justice Office: 'BradCast' 4/24/25 'Green News Report' 4/24/25
'Green News Report' 4/24/25
 Nation's Largest Broadcaster Mandates News Outlets Hoax Viewers to Help Gut FCC Rules: 'BradCast' 4/23/25
Nation's Largest Broadcaster Mandates News Outlets Hoax Viewers to Help Gut FCC Rules: 'BradCast' 4/23/25 Trump's FCC on Precipice of Ending All Limits on Corporate Control of Local TV Stations
Trump's FCC on Precipice of Ending All Limits on Corporate Control of Local TV Stations GOP Earth Day 2025 Hypocrisies and Dilemmas: 'BradCast' 4/22/25
GOP Earth Day 2025 Hypocrisies and Dilemmas: 'BradCast' 4/22/25 'Green News Report' 4/22/25
'Green News Report' 4/22/25 Pope Francis Dies,
Pope Francis Dies, Sunday
Sunday  Sunday 'Zero Day' Toons
Sunday 'Zero Day' Toons Soc. Sec. Expert Warns DOGE Hastening Collapse, Privati-zation: 'BradCast' 4/10/2025
Soc. Sec. Expert Warns DOGE Hastening Collapse, Privati-zation: 'BradCast' 4/10/2025 'Green News Report' 4/10/25
'Green News Report' 4/10/25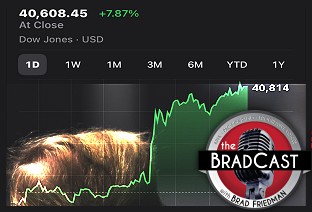 Trump Blinks, Chaos Reigns, Markets Spike as Many Tariffs Remain Despite 90-Day 'Pause': 'BradCast' 4/9/25
Trump Blinks, Chaos Reigns, Markets Spike as Many Tariffs Remain Despite 90-Day 'Pause': 'BradCast' 4/9/25 SCOTUS Deportation Ruling Grimmer Than First Appears: 'BradCast' 4/8/25
SCOTUS Deportation Ruling Grimmer Than First Appears: 'BradCast' 4/8/25 'Green News Report' 4/8/25
'Green News Report' 4/8/25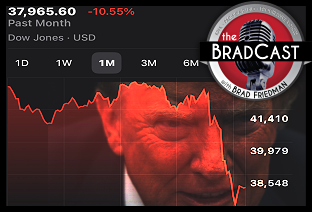 Cliff Diving with Donald: 'BradCast' 4/7/25
Cliff Diving with Donald: 'BradCast' 4/7/25 Sunday 'Don't Look Down' Toons
Sunday 'Don't Look Down' Toons 'Green News Report' 4/3/25
'Green News Report' 4/3/25 'Mob Boss' Trump's Trade Sanctions Tank U.S., World Markets: 'BradCast' 4/3/25
'Mob Boss' Trump's Trade Sanctions Tank U.S., World Markets: 'BradCast' 4/3/25 Crawford Landslide in WI; Booker Makes History in U.S. Senate: 'BradCast' 4/2/25
Crawford Landslide in WI; Booker Makes History in U.S. Senate: 'BradCast' 4/2/25 Judge Ends Challenge to GA's Unverifiable, Insecure Vote System: 'BradCast' 4/1/25
Judge Ends Challenge to GA's Unverifiable, Insecure Vote System: 'BradCast' 4/1/25 Bad Court, Election News for Trump is Good News for U.S.: 'BradCast' 3/31
Bad Court, Election News for Trump is Good News for U.S.: 'BradCast' 3/31 Vets Push Back at Plan to Slash Health Care, 80K V.A. Jobs: 'BradCast' 3/27/25
Vets Push Back at Plan to Slash Health Care, 80K V.A. Jobs: 'BradCast' 3/27/25 Signal Scandal Worsens for Trump, GOP; Big Dem Election Wins in PA: 'BradCast' 3/26
Signal Scandal Worsens for Trump, GOP; Big Dem Election Wins in PA: 'BradCast' 3/26 'Emptywheel': Trump NatSec Team Should 'Resign in Disgrace': 'BradCast' 3/25/25
'Emptywheel': Trump NatSec Team Should 'Resign in Disgrace': 'BradCast' 3/25/25 USPS 'Belongs to the People, Not the Billionaires': 'BradCast' 3/24/25
USPS 'Belongs to the People, Not the Billionaires': 'BradCast' 3/24/25
 VA GOP VOTER REG FRAUDSTER OFF HOOK
VA GOP VOTER REG FRAUDSTER OFF HOOK Criminal GOP Voter Registration Fraud Probe Expanding in VA
Criminal GOP Voter Registration Fraud Probe Expanding in VA DOJ PROBE SOUGHT AFTER VA ARREST
DOJ PROBE SOUGHT AFTER VA ARREST Arrest in VA: GOP Voter Reg Scandal Widens
Arrest in VA: GOP Voter Reg Scandal Widens ALL TOGETHER: ROVE, SPROUL, KOCHS, RNC
ALL TOGETHER: ROVE, SPROUL, KOCHS, RNC LATimes: RNC's 'Fired' Sproul Working for Repubs in 'as Many as 30 States'
LATimes: RNC's 'Fired' Sproul Working for Repubs in 'as Many as 30 States' 'Fired' Sproul Group 'Cloned', Still Working for Republicans in At Least 10 States
'Fired' Sproul Group 'Cloned', Still Working for Republicans in At Least 10 States FINALLY: FOX ON GOP REG FRAUD SCANDAL
FINALLY: FOX ON GOP REG FRAUD SCANDAL COLORADO FOLLOWS FLORIDA WITH GOP CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION
COLORADO FOLLOWS FLORIDA WITH GOP CRIMINAL INVESTIGATION CRIMINAL PROBE LAUNCHED INTO GOP VOTER REGISTRATION FRAUD SCANDAL IN FL
CRIMINAL PROBE LAUNCHED INTO GOP VOTER REGISTRATION FRAUD SCANDAL IN FL Brad Breaks PA Photo ID & GOP Registration Fraud Scandal News on Hartmann TV
Brad Breaks PA Photo ID & GOP Registration Fraud Scandal News on Hartmann TV  CAUGHT ON TAPE: COORDINATED NATIONWIDE GOP VOTER REG SCAM
CAUGHT ON TAPE: COORDINATED NATIONWIDE GOP VOTER REG SCAM CRIMINAL ELECTION FRAUD COMPLAINT FILED AGAINST GOP 'FRAUD' FIRM
CRIMINAL ELECTION FRAUD COMPLAINT FILED AGAINST GOP 'FRAUD' FIRM RICK SCOTT GETS ROLLED IN GOP REGISTRATION FRAUD SCANDAL
RICK SCOTT GETS ROLLED IN GOP REGISTRATION FRAUD SCANDAL VIDEO: Brad Breaks GOP Reg Fraud Scandal on Hartmann TV
VIDEO: Brad Breaks GOP Reg Fraud Scandal on Hartmann TV RNC FIRES NATIONAL VOTER REGISTRATION FIRM FOR FRAUD
RNC FIRES NATIONAL VOTER REGISTRATION FIRM FOR FRAUD EXCLUSIVE: Intvw w/ FL Official Who First Discovered GOP Reg Fraud
EXCLUSIVE: Intvw w/ FL Official Who First Discovered GOP Reg Fraud GOP REGISTRATION FRAUD FOUND IN FL
GOP REGISTRATION FRAUD FOUND IN FL



















 We have been reporting for at least two years now on the analysis by the plaintiffs' expert in a Georgia voting system lawsuit said to reveal vulnerabilities so alarming that the U.S. District Court judge overseeing the federal case actually sealed the report, even from the plaintiffs themselves! On today's
We have been reporting for at least two years now on the analysis by the plaintiffs' expert in a Georgia voting system lawsuit said to reveal vulnerabilities so alarming that the U.S. District Court judge overseeing the federal case actually sealed the report, even from the plaintiffs themselves! On today's  Today on
Today on  In support of his lie that the 2020 election was stolen from him, Donald Trump has been telling anyone who will listen that "thousands and thousands" of ballots have recently been discovered from the 2020 race, including in New Hampshire, where the state's Republican Governor certified his loss to Joe Biden by some 55,000 votes. But something troubling was discovered during a post-election hand-count last November in a small New Hampshire town, revealing that the state's decades-old Diebold optical-scan computer tabulators undercounted some Republican votes and overcounted some for a Democrat on the ballot. Thanks to a real (non-clown show) forensic audit in Windham, NH, which is finally wrapping up, we now know why, as explained in detail on today's
In support of his lie that the 2020 election was stolen from him, Donald Trump has been telling anyone who will listen that "thousands and thousands" of ballots have recently been discovered from the 2020 race, including in New Hampshire, where the state's Republican Governor certified his loss to Joe Biden by some 55,000 votes. But something troubling was discovered during a post-election hand-count last November in a small New Hampshire town, revealing that the state's decades-old Diebold optical-scan computer tabulators undercounted some Republican votes and overcounted some for a Democrat on the ballot. Thanks to a real (non-clown show) forensic audit in Windham, NH, which is finally wrapping up, we now know why, as explained in detail on today's  There is nothing wrong with citizens --- no matter how partisan or misinformed --- demanding to know for themselves that election results have been accurately recorded and reported. That's true even in cases where they have been blatantly lied to by, say, a disgraced, failed President of the United States. But post-election audits must be done in full public view from top to bottom, with all processes and evidence from the election kept within a transparent, well-documented, secure chain-of-custody at every step. Two ongoing post-election audits from the 2020 election are currently underway. One offers an example of exactly how not to do such a probe, the other one is shaping up to be a model for the nation.
There is nothing wrong with citizens --- no matter how partisan or misinformed --- demanding to know for themselves that election results have been accurately recorded and reported. That's true even in cases where they have been blatantly lied to by, say, a disgraced, failed President of the United States. But post-election audits must be done in full public view from top to bottom, with all processes and evidence from the election kept within a transparent, well-documented, secure chain-of-custody at every step. Two ongoing post-election audits from the 2020 election are currently underway. One offers an example of exactly how not to do such a probe, the other one is shaping up to be a model for the nation.  We've got two lede stories really on today's
We've got two lede stories really on today's  Will we ever escape the 2020 "Big Lie"? Maybe. But it's gonna take a while. That said, we've got some very good news on today's
Will we ever escape the 2020 "Big Lie"? Maybe. But it's gonna take a while. That said, we've got some very good news on today's  It's been a weekend and more of The Crazy since we last spoke. On today's
It's been a weekend and more of The Crazy since we last spoke. On today's  Join us on today's
Join us on today's  On today's
On today's  On today's
On today's  Today, we devote the bulk of
Today, we devote the bulk of  On today's
On today's  As usual, we cover far too much on today's
As usual, we cover far too much on today's  We've got some pretty huge and long-overdue breaking news today from a federal court in Atlanta. It's huge enough that we dumped what we were previously planning to cover to devote today's
We've got some pretty huge and long-overdue breaking news today from a federal court in Atlanta. It's huge enough that we dumped what we were previously planning to cover to devote today's 













